5 Common Questions About Gum Disease Treatment from a Periodontist
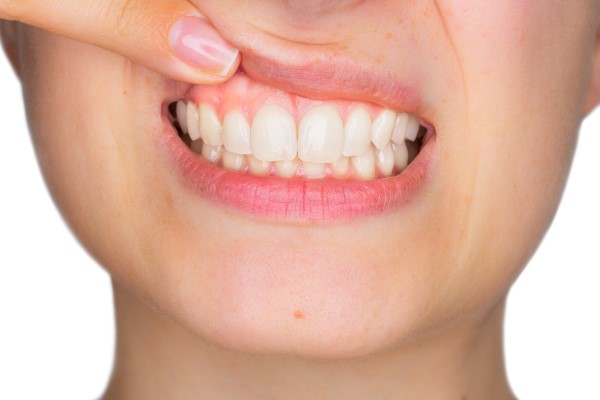
Gum disease treatment is crucial for restoring oral health and preventing periodontal disease from progressing and causing irreversible damage. A periodontist specializes in diagnosing, treating, and managing gum disease, offering expertise and care tailored to each patient's condition. Reviewing the most common questions regarding gum disease treatment can help individuals understand their appointments and care plans.
What is gum disease, and how does it develop?
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, starts with plaque buildup on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky, bacteria-filled film that forms after eating and drinking. If one does not remove this film regularly through brushing and flossing, it will harden into tartar, which they cannot remove with traditional tools. The combination of plaque and tartar irritates the gums, leading to inflammation and infection.
In the early stages, gum disease is known as gingivitis, which causes red, swollen, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, where the infection spreads deeper into the gums and affects the bone that supports the teeth. This can lead to tooth mobility and, in severe cases, tooth loss. Early intervention from a periodontist is key to stopping the progression of the disease.
What are the symptoms of gum disease?
Gum disease symptoms can vary, but they most commonly manifest as swollen or bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, receding gums, loose teeth, and changes in bite or tooth sensitivity. As the disease progresses, symptoms may worsen, leading to more significant pain and discomfort. Note that for gingivitis, the symptoms may be less noticeable, but as the disease advances, patients may experience increased discomfort and complications. If any of these signs appear, it is important to consult with a periodontist to evaluate the condition and begin appropriate gum disease treatment.
What are gum disease treatment options?
Gum disease treatment depends on the stage of the condition and its severity. Non-surgical treatments like scaling and root planing are common for gingivitis. This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooths the tooth roots to help the gums reattach to the teeth.
For more advanced stages of gum disease, additional treatments may be necessary. This could include surgical procedures such as gum grafts, where the periodontist removes healthy tissue from elsewhere in the patient's mouth and places it in the receding areas. They may also perform a bone graft for those whose disease caused alveolar bone degeneration. The procedure involves taking a synthetic bone-like material and placing it into the receded areas, allowing it to fuse with the surrounding bone tissue. No matter the procedure's invasiveness, the periodontist will likely prescribe antibiotics to help eliminate remnants of the infection.
How long will it take to recover from gum disease?
Prevention methods are crucial in managing gum disease and ensuring it does not return. Proper oral hygiene, brushing twice daily and flossing once daily, is essential in removing plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums. Regular dental checkups with a periodontist and professional cleanings every six months help detect early signs of gum disease before they develop into more serious problems.
In addition to good oral hygiene, patients should avoid smoking and maintain a balanced diet to promote gum health. Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease, as it weakens the immune system and impairs the body's ability to heal. Further, a healthy diet that includes vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, can also help support gum tissue and prevent recurring infections.
Are there prevention methods for gum disease?
Recovery time after gum disease treatment depends on the type of procedure the periodontist performs. Non-surgical treatments like scaling and root planing usually require minimal recovery time, with patients experiencing swelling, bruising, and discomfort for up to a week or more.
It is essential to follow all aftercare instructions for a few days. However, more extensive surgical treatments may take longer to heal, and patients may experience swelling, bruising, and discomfort for up to a week or more.
It is essential to follow all aftercare instructions the periodontist provides, including maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding hard or sticky foods, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor healing. The periodontist will provide specific instructions based on the gum disease treatment to ensure the recovery process is as smooth as possible.
Schedule a consultation
Gum disease treatment is essential for preserving oral health and preventing the progression of periodontal disease. Through early diagnosis and effective treatment, you can take control of the disease. Contact Cumming's Family Dentist if you have more questions or show signs of gum disease.
Request an appointment here: https://cummingsfamilydentist.com or call Cumming's Family Dentist at (770) 280-8723 for an appointment in our Cumming office.
Related Posts
Receding gums can affect your confidence and leave you feeling self-conscious, even when you have every reason to smile. Luckily, a dentist can correct gum recession and its root cause. They can craft treatment plans that best suit their patients’ needs. A treatment plan will include one or more procedures to restore the looks and…
Concerned about gum recession? Read on to learn the commonality of receding gums and how they can be treated and prevented. Receding gums are common among individuals with periodontal disease. However, there are different levels of gum recession, and the severity of the concerns depends on how far the gums have receded.Receding gums can become…
Receding gums are usually a scary and painful condition. It helps to be aware of the symptoms of gum recession as well as how to avoid them. Various issues may cause gum recession, but individuals who smoke or use tobacco regularly are more prone to it. Continue reading to learn more about why this is…
Receding gums leave the teeth roots vulnerable to the harmful elements that reside in or pass through your mouth. Medication can help limit the damage caused by gum infections, slowing down gum recession.Unlike the visible section of the teeth, your tooth roots lack an enamel layer. Their protection from acids in the mouth comes from…
